What is a Jaw Crusher Used For?
Jaw crushers are indispensable machines in various industrial applications, renowned for their capability to crush large rocks and materials into smaller fragments. These powerful devices are pivotal in industries such as mining, construction, and recycling, where the initial reduction of material size is crucial for further processing.
What is a Jaw Crusher Used For?
A. Primary Crushing in Mining and Quarrying
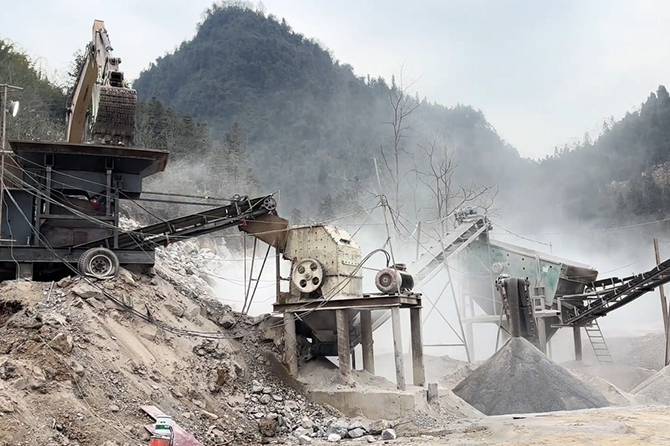
Jaw crushers are often the first stage in the crushing process in mining and quarrying. They are designed to handle large feeds of rocks and minerals, breaking them down into smaller, more manageable sizes. This initial reduction is crucial for subsequent processing stages, such as grinding and sizing, which are necessary for extracting valuable minerals.
B. Construction and Aggregate Production
In the construction industry, jaw crushers are vital for producing aggregates, which are essential for creating various building materials. Crushed stone and gravel are commonly used in concrete, asphalt, and road construction. By crushing rocks into uniform sizes, jaw crushers ensure the quality and consistency of these materials.
C. Recycling Industries
The recycling industry increasingly relies on jaw crushers to process a wide range of materials, including glass, metal, and plastics. By breaking down these materials into smaller pieces, jaw crushers facilitate easier separation and recycling, contributing to sustainable resource management.
D. Metallurgy and Ore Dressing
In metallurgy, jaw crushers are used to prepare ores for further processing. By reducing the ore to a suitable size, they enable more efficient extraction of metals through processes like flotation and smelting.


Types of Jaw Crushers
A. Jaw Crusher Machine
The standard jaw crusher machine is a stationary device renowned for its durability and high throughput capacity. Featuring a robust build, it is capable of handling large volumes of material, making it a preferred choice for large-scale mining and construction projects.
B. Mini Jaw Crusher
Mini jaw crushers are compact and designed for smaller operations or laboratory use. Despite their size, they offer efficient crushing capabilities, ideal for research, testing, or small-scale production needs.
C. Mobile Jaw Crusher
Mobile jaw crushers offer the advantage of on-site processing, eliminating the need to transport materials to a fixed crushing plant. Their mobility enhances operational flexibility, reducing costs and increasing efficiency in various applications.
D. Portable Jaw Crusher
Portable jaw crushers are designed for ease of movement and quick setup, making them ideal for remote locations or temporary crushing needs. Their versatility allows them to adapt to different site conditions, providing flexibility in material processing.
Advantages of Using Jaw Crushers
A. Efficiency and Reliability
Jaw crushers are engineered for high performance, ensuring efficient material reduction with minimal energy consumption. Their sturdy construction and reliable operation minimize downtime, making them a dependable choice for continuous production processes.
B. Cost-Effectiveness
Investing in a jaw crusher offers significant cost benefits. Despite the initial capital investment, their durability and low maintenance requirements result in long-term cost savings. Additionally, their ability to process large quantities of material efficiently reduces operational expenses.
C. Versatility
One of the key advantages of jaw crushers is their versatility. They can handle various materials, from hard rocks to recycled aggregates, and are adaptable to different crushing needs. This flexibility makes them a versatile solution across multiple industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, jaw crushers remain essential in numerous industrial applications, providing efficient and reliable material processing solutions. With advancements in technology, future jaw crushers are likely to offer even greater efficiency, sustainability, and adaptability, further solidifying their importance in various sectors.